Ransomware - Effective prevention strategies
Estimating organizations' readiness to defend against ransomware campaigns and attacks using Attack Path Workflow Analysis.

Introduction
Ransomware is a significant issue that many companies face today. WithSecure has observed substantial impacts on enterprise environments due to ransomware-related attacks. While it is undeniably a threat, the risk can be greatly mitigated with a well-defined defensive strategy. We have outlined ransomware prevention strategies and proactive measures that can help reduce the risk of an attack. The approach below will help organizations estimate their readiness.
Attack Path Workflow Analysis has three primary objectives:
- Objective 1 : Prevent Threat Actors from getting in
- Objective 2 : Prevent Threat Actors from escalating their privileges
- Objective 3 : Protect critical data from access and destruction
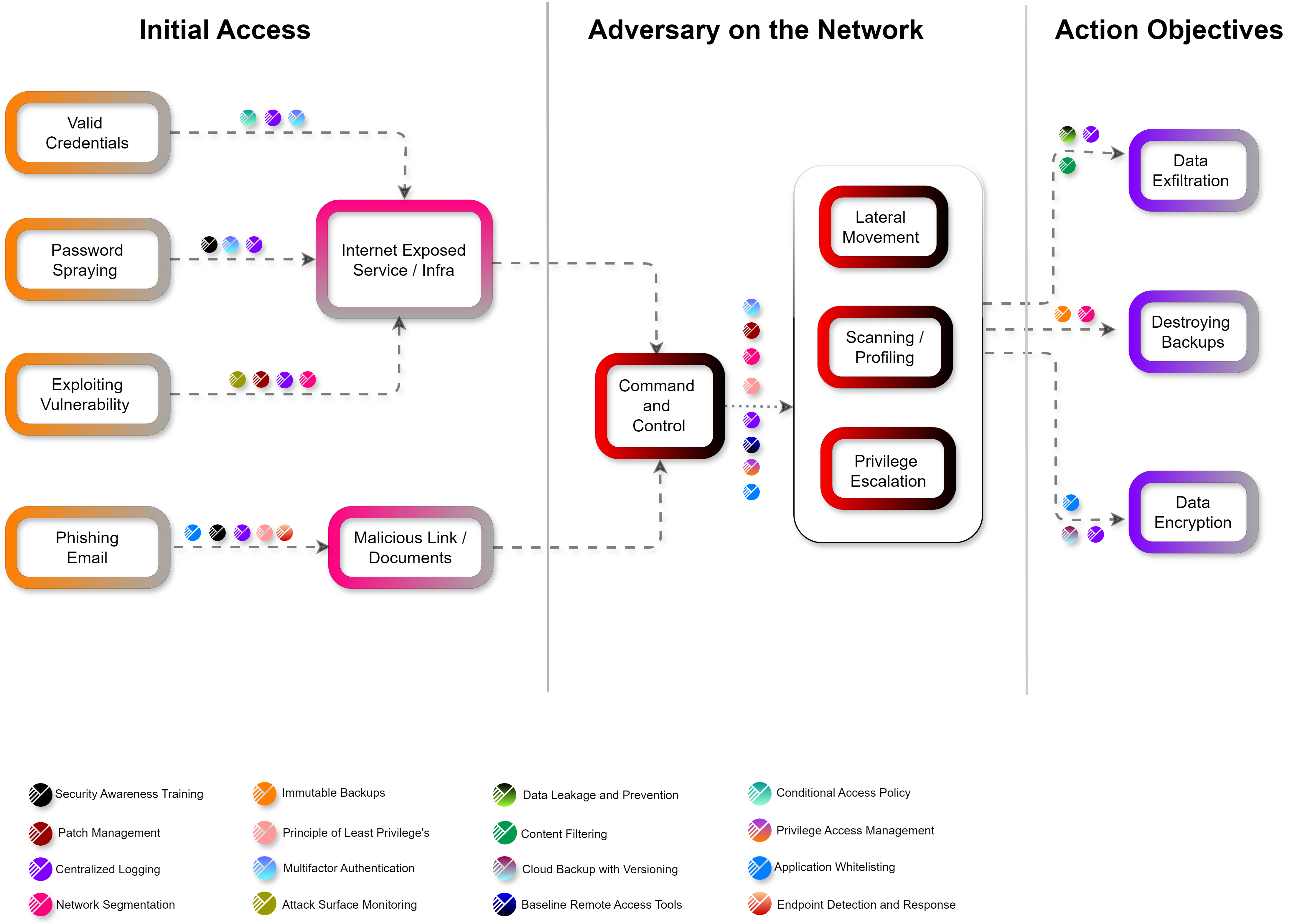 A typical attack path workflow for ransomware Incidents
A typical attack path workflow for ransomware Incidents
Detection and prevention strategies
The section below summarizes each detection and prevention approach, as well as its mapping within the MITRE D3FEND framework.
Security awareness training
Users should be educated on how to identify threats such as phishing emails, including the actions required when they receive such suspicious messages. Phishing awareness education should not only provide users with materials or courses, but also periodic evaluations to assess their proficiency in handling phishing emails and campaigns. It is essential to evaluate staff competency to ensure that all employees meet the company's standards for corporate security policies.

Patch management
Poor patching practices can leave systems vulnerable to attack for extended periods, representing a significant risk to the organization. Implementing mature patching policies and procedures ensures that all servers, workstations, and other equipment on the network are up to date and free from known vulnerabilities. Priority should be given to resources accessible from the Internet.

Immutable backups
In most ransomware attacks, threat actors attempt to delete critical backups to ensure that no restore points are available. Having immutable backups has become crucial for recovery, as immutable backup data is protected from potential changes or deletions. These backups can only be deleted after a specified retention period has expired.

Centralized logging
Wherever possible, logs such as Windows event logs from all servers and workstations, proxy logs, firewall logs, VPN authentication logs, AV detection logs, Office 365 audit logs, and any other relevant logs, should be shipped to a secure and centralized location, ideally within an SIEM (e.g., Microsoft Sentinel). This data retention should be maintained for as long as financially feasible, but for at least 90 days to provide a rolling body of evidence for incident investigation.

Network segmentation
Segmenting a network is often one of the most effective ways to slow down attackers, as it significantly limits their actions. The requirements for each segment should be fully documented, and the network segmentation plan should be designed accordingly. Systems and applications should be grouped by function, with additional separation applied to where differences in trust zones exist. Priority should be given to segmenting systems that could have the most negative impact on the business if breached.

Date leakage prevention
Ransomware threat actors are increasingly using extortion techniques to pressure organizations into paying ransoms. Implementing a robust data lifecycle management system, supported by data leakage prevention technology, can help identify data theft in many cases.

Principle of least privilege
This is a concept that maintains a user or entity should only have access to the specific data, resources, and applications needed to complete their tasks. By following this principle, organizations can reduce their attack surface and slow down activities such as lateral movement and malware spreading.

Multifactor Authentication
One effective way to reduce account compromise is to require multi-factor authentication methods. A best practice is to require any two of the following:
- Something the user knows, typically a password.
- Something they have, such as a trusted device that is not easily duplicated, like a phone or hardware token.
- Something the user is, such as a fingerprint or face scan.
It's important to note that while MFA is not a foolproof approach to security, it does reduce the risk of shared or leaked credentials being utilized. This provides an additional layer of protection beyond just a username and password, making it much more difficult for threat actors to gain access to sensitive information.

Application Allowlist
To reduce the attack surface, organizations should take steps to limit the execution of unknown files, especially those downloaded from the internet. This can be achieved using block and allow lists in endpoint solutions. This basic hygiene on the endpoints helps the organization contain security breaches by preventing unapproved software from running in the environment.

Attack Surface Monitoring
Since large environments change frequently, it is recommended to have a regular review schedule, at least once per month. This schedule allows for the identification of newly discovered services, which can then be assessed for vulnerabilities and removed if necessary. Additionally, frequent vulnerability scans of the perimeter should be performed. This process primarily ensures that no unnecessary services are publicly exposed and secondarily verifies that no vulnerable services are exposed to the internet.

Content Filtering
A content filtering solution, such as a web proxy, sits between end users and the internet, applying controls over the websites that can be accessed and the files that can be downloaded. This solution blocks attempts to visit malicious websites where phishing pages are hosted and also prevents threat actors from exfiltrating data to known cloud storage locations.

Cloud Backup with Versioning
Data can reside anywhere on the enterprise network, including employees' endpoints. If a ransomware attack is successful, the ransomware will hold critical files hostage and deny access until a ransom is paid. While cloud backup solutions with unlimited file versioning won’t prevent ransomware attacks, they can help recover critical files, potentially eliminating the need to pay a ransom.

Baseline Remote Access Tools
Threat actors often use remote access tools to connect to a compromised environment, and they frequently attempt to use tools already employed by the victim to blend in and avoid raising suspicion. Therefore, it is crucial to establish a baseline for such access and determine which applications are authorized for use. Tools that are not currently in use should be blocked, and the individuals authorized to use them should be clearly defined.

Endpoint detection and response
A number of opportunities to detect intrusions in the early stages were missed due to limited detection capabilities and/or a lack of continuous monitoring on endpoints. This capability can be achieved through the diligent implementation of EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) technology alongside EPP (Endpoint Protection) across all endpoints in the environment. This approach allows organizations to track and trace activities within the environment and respond to malicious or suspicious behaviour before threat actors can escalate their privileges.

Privilege Access Management
Privileged Access Management (PAM) is an identity solution designed to protect against cyber threats by monitoring, detecting, and preventing unauthorized privileged access to critical resources. Limiting the number of users with administrative access enhances system security, while additional layers of protection help mitigate data breaches by threat actors. Some of the key features include:
- Providing just-in-time access to critical resources
- Allowing secure remote access using encrypted gateways instead of passwords
- Monitoring privileged sessions to support investigative audits
- Analyzing unusual privileged activity that might be harmful to your organization

Conditional Access Policy
Conditional Access policies provide a framework for implementing access controls based on predefined conditions. These policies enable organizations to define and enforce specific access requirements, such as multi-factor authentication (MFA), device compliance, location-based restrictions, and more. The primary objective of using Conditional Access policies is to mitigate risks associated with unauthorized access and data breaches. By applying specific conditions and requirements, organizations can ensure that only trusted users with compliant devices and appropriate permissions are granted access to critical resources.
